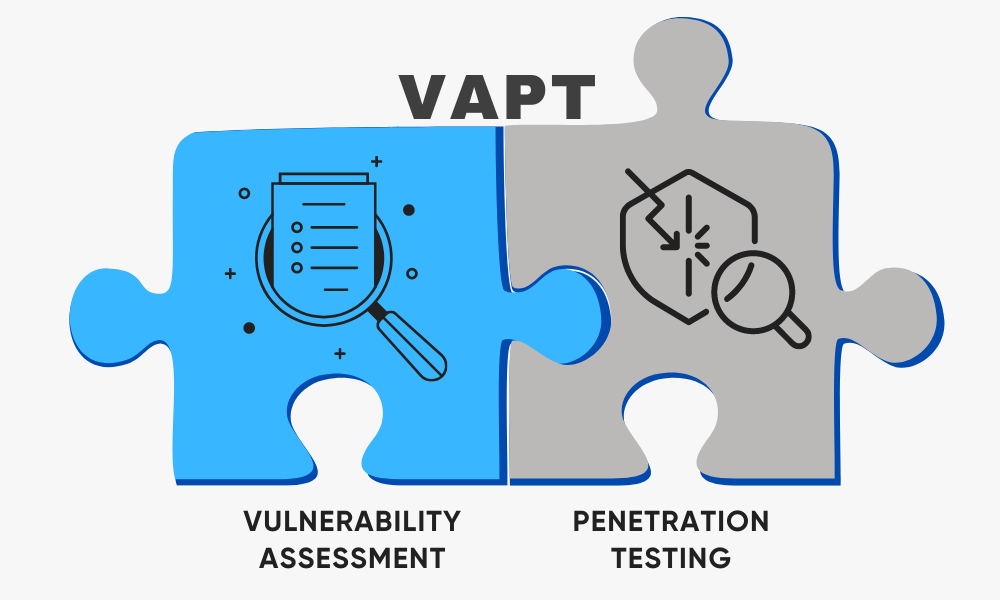
Two essential techniques for enhancing security are Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT). These processes serve different but complementary functions and play a critical role in a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
🤔 Understanding Vulnerability Assessment
A Vulnerability Assessment is a methodical process that involves identifying and classifying vulnerabilities in a network, system, or application. The primary goal of a vulnerability assessment is to detect weaknesses in the security posture of an organization that could potentially be exploited by attackers. While the process focuses on identifying known vulnerabilities, it does not simulate actual attacks.
Types of Vulnerability Assessments.
There are several types of vulnerability assessments, each tailored to specific parts of an organization’s IT environment:
▪️Network-based assessments. This type of assessment focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in network infrastructure, including firewalls, routers, and switches. It helps detect open ports, weak configurations, or outdated software that could expose the network to external threats.
▪️Host-based assessments. Host-based vulnerability assessments examine individual devices such as servers, workstations, or mobile devices for vulnerabilities like missing patches, misconfigurations, or weak authentication mechanisms.
▪️Application-based assessments. These assessments analyze the security of web applications and software, identifying vulnerabilities like cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection, or insecure API configurations.
▪️Wireless assessments. Wireless assessments focus on identifying vulnerabilities in wireless networks, such as weak encryption protocols or unauthorized access points.
▪️ Database assessments. Database assessments evaluate the security of databases by identifying misconfigurations, weak permissions, and outdated software versions that could be exploited to access sensitive data.
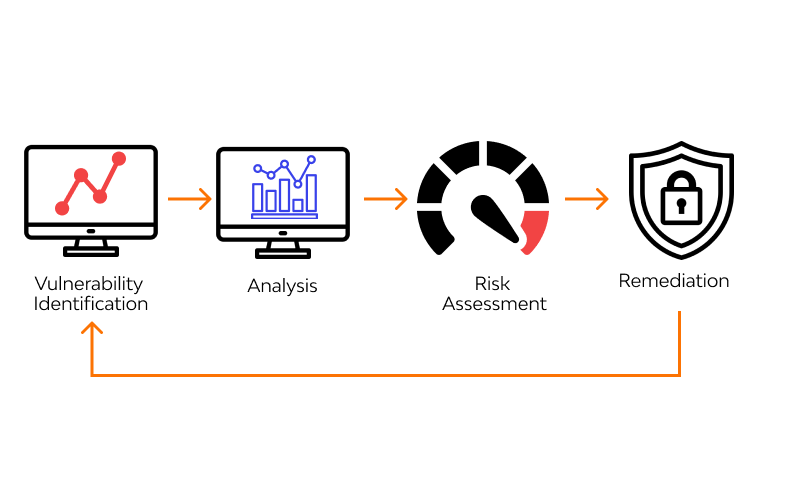
The Vulnerability Assessment Process.
A vulnerability assessment typically follows a structured process that ensures comprehensive identification and analysis of vulnerabilities.
The key steps involved include:
▪️ Asset discovery and inventory. Before scanning for vulnerabilities, it’s essential to identify and inventory all critical assets within the environment. This includes hardware, software, and data that require protection. Asset discovery tools help automate this process by scanning the network for devices, services, and applications.
▪️ Vulnerability scanning. During this phase, automated tools like Nessus, OpenVAS, or Qualys are used to scan the environment for known vulnerabilities. These tools rely on regularly updated vulnerability databases that catalog thousands of potential security flaws. The scan identifies weaknesses such as unpatched software, outdated protocols, weak encryption standards, or misconfigurations.
▪️ Vulnerability classification and prioritization. After vulnerabilities are identified, they are classified based on severity and impact. Tools often use industry-standard scoring systems such as the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which provides a numerical value (from 0 to 10) to indicate the severity of a vulnerability. Prioritizing vulnerabilities is crucial to ensure that the most critical threats are addressed first.
▪️ Reporting and recommendations. The findings of the vulnerability assessment are compiled into a detailed report, which includes information on the vulnerabilities discovered, their potential impact on the organization, and recommendations for remediation. These reports provide valuable insights for IT and security teams to take corrective actions.
▪️ Remediation and mitigation. Remediation involves fixing the identified vulnerabilities, often by applying software patches, reconfiguring systems, or upgrading outdated components. In cases where immediate remediation is not possible, mitigating controls such as firewalls or intrusion detection systems (IDS) can be implemented to reduce the risk of exploitation.
Vulnerability Assessment Tools.
A variety of tools are available to perform vulnerability assessments.
Some of the most widely used include:
Nessus - a highly popular vulnerability scanner that supports a wide range of systems and provides comprehensive reports on vulnerabilities.
OpenVAS - an open-source vulnerability scanner that is part of the Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) framework.
Qualys - a cloud-based security platform offering vulnerability scanning, compliance monitoring, and web application scanning.
Rapid7 Nexpose - a vulnerability management tool that offers real-time vulnerability tracking and provides recommendations for remediation.
✅ Advantages of Vulnerability Assessments.
▪️Continuous Monitoring. Vulnerability assessments can be scheduled regularly to monitor the evolving threat landscape and detect new vulnerabilities as they emerge.
▪️Cost-Effective. Since vulnerability assessments are mostly automated and can be done in-house, they offer a cost-effective solution for identifying security weaknesses.
▪️Compliance. Many regulatory standards, such as GDPR, PCI-DSS, and HIPAA, require organizations to perform regular vulnerability assessments to maintain compliance.
▪️Low Risk. Vulnerability assessments do not actively exploit vulnerabilities, so there is minimal risk of disrupting operations during the assessment process.
What is Penetration Testing?
While a vulnerability assessment identifies potential weaknesses, Penetration Testing (commonly referred to as pen testing) simulates a real-world attack to exploit those vulnerabilities and determine the actual risk they pose. Penetration testing is more intrusive than vulnerability assessment because it involves actively trying to breach an organization's security defenses. The goal is to simulate an attacker’s behavior and determine how effectively the organization’s systems can withstand a cyberattack.
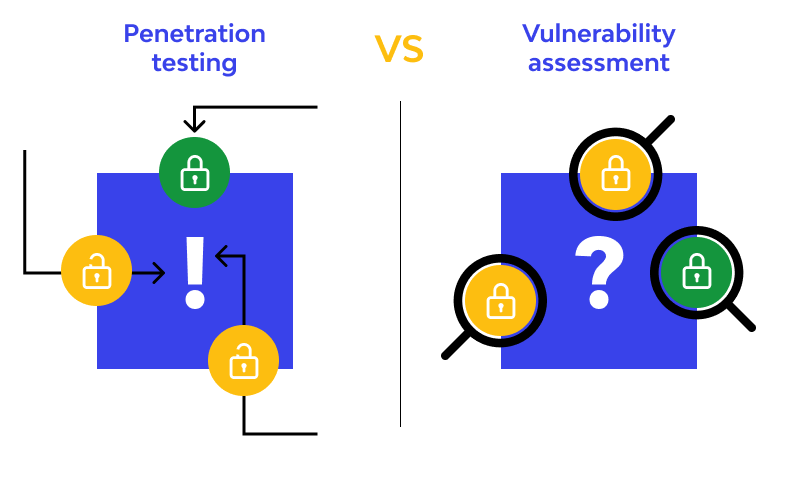
Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing: Key Differences
While both vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are essential for a comprehensive security strategy, it serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics:
Focus:
Vulnerability Assessment. Focuses on identifying and cataloging known vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems. It does not involve actively exploiting these vulnerabilities.
Penetration Testing. Focuses on exploiting vulnerabilities to simulate a real-world attack, showing how attackers could gain unauthorized access or cause harm.
Approach:
Vulnerability Assessment. Primarily relies on automated tools and databases of known vulnerabilities. It’s more of a passive approach aimed at identifying potential security issues.
Penetration Testing. Involves both manual and automated techniques to simulate an attack, making it an active and intrusive approach.
Risk Level:
Vulnerability Assessment. Since it doesn’t involve exploitation, it poses minimal risk to business operations or systems during the assessment.
Penetration Testing. Pen testing can potentially cause disruptions to services or systems, especially when exploiting vulnerabilities, so it needs to be carefully planned and monitored.
Output:
Vulnerability Assessment. Provides a list of vulnerabilities categorized by severity and recommendations for remediation.
Penetration Testing. Provides a detailed account of how vulnerabilities were exploited, the extent of the compromise, and insights into what an attacker could achieve with access.
Frequency:
Vulnerability Assessment. Can be performed regularly, sometimes even continuously, as part of routine security operations.
Penetration Testing. Typically conducted less frequently, perhaps annually or semi-annually, given its complexity and the potential for disruptions.
Cost:
Vulnerability Assessment. Generally more cost-effective because it relies on automated tools, making it scalable for regular use.
Penetration Testing. More expensive due to the manual effort involved and the need for specialized expertise to simulate sophisticated attacks.
How Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing Work Together
While vulnerability assessments and penetration testing serve different purposes, they are most effective when used together as part of a holistic security strategy. The combination of these two approaches provides a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s security posture.
▪️Vulnerability Assessment as a Starting Point. Regular vulnerability assessments help identify potential weaknesses in an organization’s IT infrastructure. These assessments serve as the first line of defense, helping organizations detect and address common vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
▪️Penetration Testing for Deeper Insight. Once vulnerabilities have been identified, penetration testing provides a deeper understanding of the actual risks posed by those vulnerabilities. Pen testing reveals how an attacker might exploit weaknesses, what the impact of a successful breach could be, and whether current defenses are sufficient.
▪️Continuous Improvement. The combination of vulnerability assessments and penetration testing enables organizations to continuously improve their security measures. Vulnerability assessments provide the foundation for ongoing monitoring, while periodic penetration tests ensure that critical vulnerabilities are addressed and that the overall security posture remains strong.
▪️Compliance and Risk Management. Many regulatory frameworks and industry standards, such as PCI-DSS, ISO 27001, and NIST, require organizations to conduct both vulnerability assessments and penetration testing as part of their risk management strategies. Integrating both processes helps organizations stay compliant and ensures that they are taking a proactive approach to security.
🚫 Common Challenges in VAPT Implementation
Implementing an effective Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing (VAPT) program can be challenging for organizations, especially those with limited resources or expertise.
Some common challenges include:
▪️Resource Constraints. Smaller organizations may lack the personnel, tools, or budget needed to conduct regular vulnerability assessments and penetration tests. In such cases, outsourcing these services to third-party providers can be a viable solution.
▪️Skill Gaps. Penetration testing requires a high level of technical expertise, and many organizations struggle to find qualified security professionals who can conduct thorough and effective tests.
▪️Balancing Security with Business Operations. Penetration testing can cause disruptions to services or operations, especially when vulnerabilities are actively exploited. Organizations must carefully plan tests to minimize the impact on critical business functions.
▪️Evolving Threat Landscape. New vulnerabilities are discovered every day, and attackers continue to develop more sophisticated techniques. Organizations must stay vigilant and continuously update their vulnerability assessment and penetration testing processes to keep pace with the evolving threat landscape.
Best Practices for Implementing VAPT
To ensure the effectiveness of vulnerability assessments and penetration testing, organizations should follow these best practices:
▪️Define Clear Objectives. Establish the goals of the VAPT program, including the specific assets and systems to be assessed, the scope of the tests, and the expected outcomes. Defining clear objectives ensures that the assessment and testing efforts are aligned with business priorities.
▪️Use a Risk-Based Approach. Prioritize vulnerability assessments and penetration testing based on the organization’s risk profile. Critical systems, applications, and data that are most likely to be targeted by attackers should be tested first.
▪️Automate Where Possible. Leverage automation tools for vulnerability assessments to ensure that systems are continuously monitored for new threats. While penetration testing requires manual effort, automated vulnerability scanning can provide regular insights and help identify new weaknesses between pen testing engagements.
▪️Engage Qualified Experts. Ensure that vulnerability assessments and penetration tests are conducted by qualified professionals with experience in cybersecurity. For penetration testing, consider using external third-party experts to gain an unbiased perspective.
▪️Document and Review. Thoroughly document the results of both vulnerability assessments and penetration tests. Regularly review these reports with security and IT teams to ensure that remediation efforts are tracked and completed in a timely manner.
▪️Conduct Follow-Up Testing. After remediation efforts are made, conduct follow-up testing to ensure that the identified vulnerabilities have been addressed. Re-testing is essential to verify that vulnerabilities have been properly fixed and that no new security gaps have been introduced.
Conclusion
In the fight against cyber threats, vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are critical tools for identifying and mitigating security risks. By integrating both approaches into a comprehensive security strategy, organizations can proactively identify weaknesses, address critical vulnerabilities, and ensure that their defenses are resilient against both known and unknown threats.
Vulnerability Assessments provide continuous monitoring and early detection of potential issues, while Penetration Testing offers a realistic assessment of how well an organization’s defenses can withstand an attack.
Contact us by providing your email address and the domain you want to test to receive a free consultation and a list of services for your first security assessment. If no vulnerabilities are found, you will receive a "Verified by A42" certificate. If critical vulnerabilities are identified, we will provide a detailed report and recommend further actions.
Email: [email protected]