Automated vulnerability scanning is one of the most common methods for checking and strengthening security controls. There is a perception that using automated vulnerability scanners can replace comprehensive penetration testing.
Organizations with limited budgets often rely on automated vulnerability scanning to cut security expenses. While this approach is understandable, it is not recommended. This article explores how automated vulnerability scanning works, its pros, cons, and possible practices.
🤔 What is Automated Vulnerability Scanning?
Automated vulnerability scanning uses specialized tools to identify and assess security weaknesses in a system. These weaknesses can include software bugs, misconfigurations, and outdated versions. The scanning process is essential for maintaining a secure environment by quickly detecting and prioritizing vulnerabilities.
Examples of tools: Nessus, Qualys, OpenVAS, Rapid7 InsightVM.
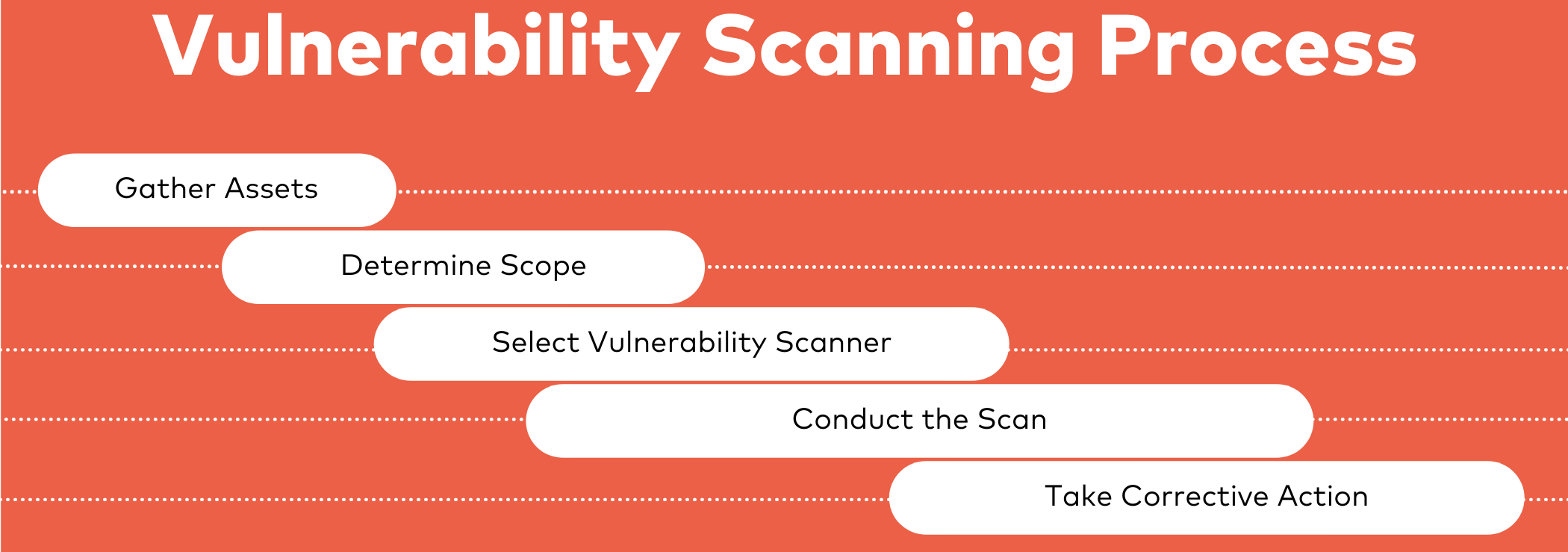
The Process of Automated Vulnerability Scanning
Now that we have understood what automated vulnerability scanning is, let’s look at the general process.
Step 1: Discovery.
The first step in automated vulnerability scanning is asset discovery. Scanners identify all assets within the digital infrastructure, including servers, workstations, and network devices. Techniques such as IP scanning and port scanning are employed to map the network and uncover all connected devices. This initial step ensures that no asset is overlooked, forming the basis for a thorough security assessment.
Step 2: Vulnerability Detection.
Once assets are identified, the scanner proceeds to detect vulnerabilities. Automated tools utilize extensive databases, such as the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) database, to check for known vulnerabilities associated with the identified assets. Various scanning methods, including network scanning and web application scanning, are employed to uncover potential security issues. By cross-referencing assets against a vast array of known vulnerabilities, organizations can quickly identify weaknesses in their systems.
Step 3: Reporting.
After the scanning process is complete, the system compiles the findings into comprehensive reports. These reports are crucial for understanding the current security posture and include detailed descriptions of identified vulnerabilities, their severity, and suggested remediation actions. The format of these reports can vary, ranging from visual dashboards for quick overviews to in-depth documents for detailed analysis, facilitating informed decision-making.
✅ Benefits of Automated Vulnerability Scanning
1. Speed and efficiency
One of the standout benefits of automated vulnerability scanning tools is their ability to deliver results quickly. This speed enables businesses to swiftly detect overlooked vulnerabilities, like misconfigurations, which, if unaddressed, could lead to significant security breaches. The rapid creation of comprehensive reports ensures that organizations are more likely to take timely action to minimize potential damage.
2. Consistency and repeatability
Undoubtedly, the speed of obtaining security ratings is the main advantage, but consistency is no less important. Organizations have full control over how frequently they run scans, whether on a regular schedule for ongoing monitoring or as needed in response to specific security concerns. This repeatability ensures that any new threats or system changes are continually assessed, providing a reliable way to maintain up-to-date defenses.
3. User-friendly interfaces
Automated vulnerability scanning software is designed to be accessible, even for users without deep technical expertise. With intuitive user interfaces, these tools simplify the scanning process and make threat analysis more approachable. Once a threat is detected, the software often performs risk modeling to determine the severity and generates easy-to-understand reports. By categorizing vulnerabilities into different risk levels, businesses can quickly prioritize which threats require immediate attention. This user-friendly design allows organizations to implement security measures systematically, even if they do not have a dedicated cybersecurity team, although having professional oversight is always a best practice.
🚫 Limitations and Challenges
1. Inability to detect all vulnerabilities
While automated vulnerability scanning tools leverage frequently updated threat databases to identify known threats, this reliance also exposes one of their most significant weaknesses. These scanners are effective only against vulnerabilities that have been previously discovered and documented. As a result, they fail to provide protection against newly emerging threats that have yet to be cataloged.
Cybersecurity is a constant race between defenders and attackers. As security experts identify and document one threat, cybercriminals are already working on developing new and more sophisticated methods of attack. This dynamic creates a perpetual lag between the emergence of threats and the scanner's ability to recognize them.
Additionally, some vulnerabilities may be too complex or have attack vectors that are not easily detectable by the current generation of scanning technology. For example, scanners often struggle with vulnerabilities that involve advanced exploitation techniques or multi-stage attacks that require a more nuanced understanding of system behavior. This limitation means that even well-maintained and updated scanning tools may overlook critical security flaws, leaving organizations vulnerable.
2. False Positives
Another common challenge with automated vulnerability scanning is the generation of false positives. Vulnerability scanners sometimes misinterpret benign network traffic or system behavior as a potential threat, flagging it as a vulnerability. This problem arises because scanners are limited by the amount of information they can access and often lack comprehensive context about the systems they are analyzing.
Without detailed endpoint authentication data or the ability to interpret network behavior fully, scanners rely on superficial analysis, which can lead to inaccurate results. The complexity of modern IT environments exacerbates this issue, and distinguishing between legitimate threats and false alarms often requires human intervention.
Moreover, most scanning tools do not come with built-in mechanisms for expert review or support from cybersecurity professionals. Without this expertise, organizations must sift through potentially hundreds of alerts to determine which ones require action, a task that can be resource-intensive and prone to error. Hiring an experienced cybersecurity professional to analyze these results and identify real threats can help, but this approach can be costly, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited budgets. Despite the expense, it is often necessary to achieve a robust security posture.
3. Limited context on impact and mitigation
Automated scanners not only struggle with detecting all threats but also often fail to provide detailed information on the implications of the vulnerabilities they uncover. When a scanner identifies a vulnerability, it typically provides a basic description of the issue and some generic recommendations for mitigation. However, it rarely explains the broader operational or business impact of the vulnerability or offers insights into long-term prevention strategies.
Organizations are then left to figure out how a particular vulnerability might affect their operations, what data could be at risk, and how to implement measures to prevent similar issues in the future. These limitations mean that automated reports must be supplemented by expert analysis to turn raw data into actionable security improvements. This analysis might involve assessing how a vulnerability could be exploited in a real-world attack, evaluating the potential financial or reputational damage, and devising strategies for ongoing risk management.
Strategies for Reducing False Positives
As organizations increasingly rely on automated vulnerability scanning to bolster their cybersecurity defenses, the challenge of managing false positives becomes a significant concern.
Reducing false positives in automated vulnerability scanning requires a multifaceted approach. First, proper tool calibration is essential. Even the most advanced tools can produce a high volume of false positives if they are not correctly configured. Understanding your scanner's settings and adjusting them based on your specific application context can significantly mitigate this issue.
Another effective strategy is to correlate findings from multiple scanning tools. This process involves comparing results from different scanners, allowing for a more accurate identification of genuine vulnerabilities and reducing fatigue from false alerts. However, this method may not always be effective, as some tools may report entirely false positives.
Integrating threat modeling into your Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) can also lead to better insights into potential attack vectors, helping to focus testing efforts more accurately and ultimately resulting in fewer false positives.
Best Practices for Effective Automated Vulnerability Scanning
While automated vulnerability scanning has its limitations, following best practices can enhance its effectiveness and help organizations mitigate security risks.
Here are some key strategies:
▪️ Regularly Update the Scanning Tool.
Ensure that your automated scanner is frequently updated to include the latest threat databases. This practice helps the tool recognize newly discovered vulnerabilities and adapt to evolving attack vectors.
▪️ Combine Scanning with Manual Oversight.
To address the issue of false positives and missed vulnerabilities, it’s essential to complement automated scans with human expertise. Engaging cybersecurity professionals to interpret scan results and analyze network traffic can significantly improve the accuracy of vulnerability assessments.
▪️ Schedule Frequent Scans.
Take advantage of the ability to conduct scans at regular intervals. By implementing a consistent scanning schedule, organizations can promptly identify and remediate vulnerabilities as they arise, reducing the window of exposure to potential attacks.
▪️ Focus on Contextual Analysis.
While automated scanners provide basic vulnerability reports, organizations should seek to understand the implications of each identified issue. Assess the potential business impact of vulnerabilities and prioritize remediation efforts based on the risk they pose to the organization.
▪️ Integrate Scanning with Other Security Measures.
Use automated scanning as part of a broader cybersecurity strategy that includes continuous monitoring, penetration testing, and threat intelligence. This holistic approach helps ensure comprehensive protection against both known and unknown threats.
▪️ Educate Staff on Security Practices.
Encourage a culture of security awareness within the organization. Regular training can help staff recognize potential threats and understand the importance of timely reporting and remediation of vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
While automated vulnerability scanning and continuous monitoring can significantly enhance an organization's cybersecurity posture, they are far from infallible. The limitations discussed—ranging from their inability to detect unknown or complex threats to the frequent occurrence of false positives and lack of contextual analysis—highlight the need for a more balanced approach. Relying solely on automated tools may give a false sense of security, as even a single misconfiguration or overlooked vulnerability could have catastrophic consequences.
A more robust solution would be to combine automated vulnerability scanning with continuous penetration testing and human expertise. Penetration testers can think like attackers, exploring sophisticated methods to breach systems and uncover vulnerabilities that scanners might miss. This combination of automation and human intelligence can create a more comprehensive security strategy, ensuring that organizations are better equipped to defend against both known and unknown threats.
Contact us by providing your email address and the domain you want to test to receive a free consultation and a list of services for your first security assessment. If no vulnerabilities are found, you will receive a "Verified by A42" certificate. If critical vulnerabilities are identified, we will provide a detailed report and recommend further actions.
Email: [email protected]