In January 2025, Chinese AI startup DeepSeek experienced a significant security breach due to an unsecured external perimeter, leading to the exposure of sensitive data. A publicly accessible ClickHouse database was left open without authentication, allowing unrestricted access to internal data.
Technical Details
The exposed database was hosted on subdomains oauth2callback.deepseek.com and dev.deepseek.com, accessible through ports 8123 and 9000.
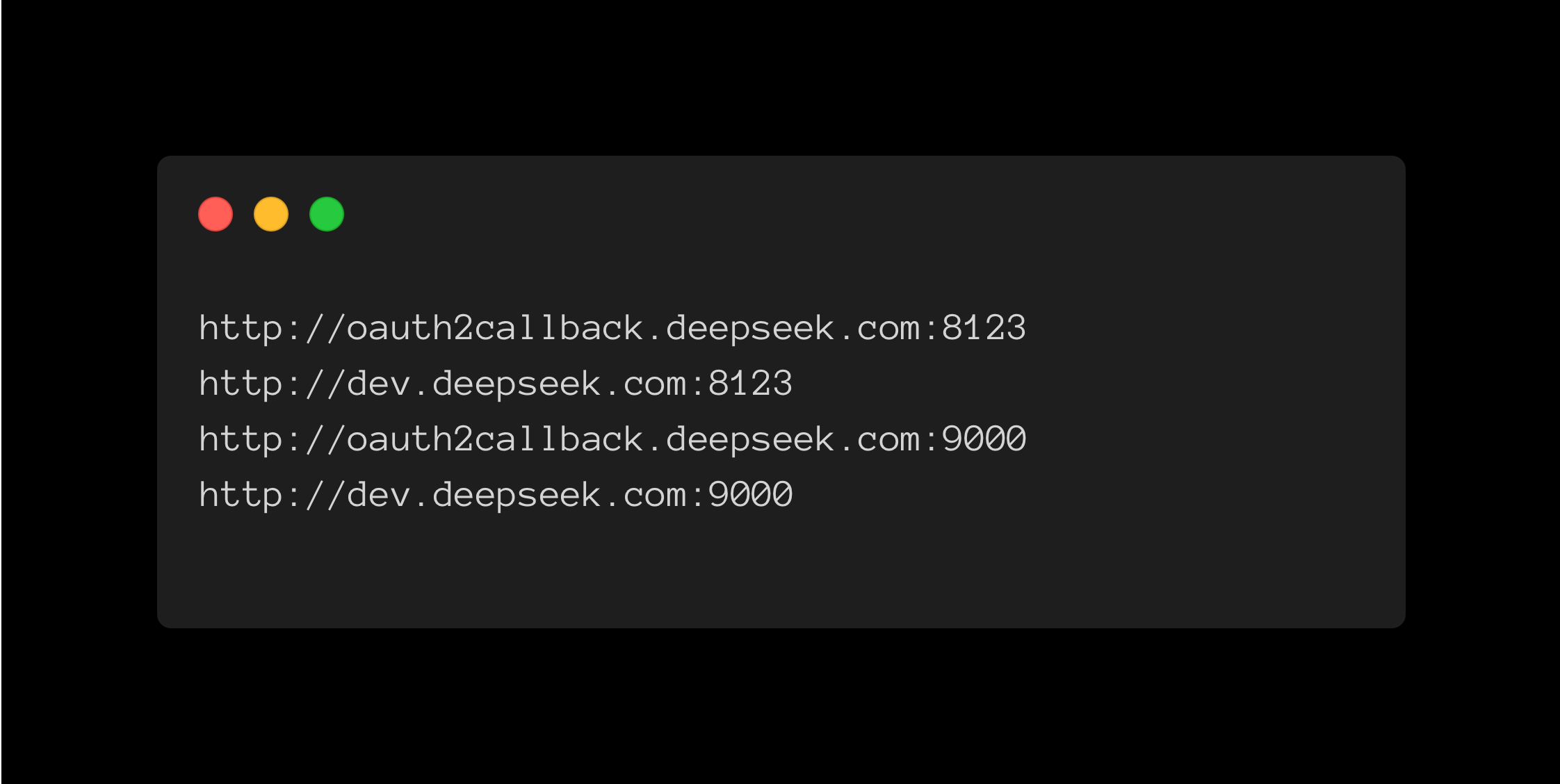
Within minutes of initiating a security assessment, researchers discovered that these ports led to an unauthenticated ClickHouse database. By accessing the /play path of ClickHouse's HTTP interface, they could execute arbitrary SQL queries, revealing a table named . This table contained over a million log entries, including:
1. Timestamps dating from January 6, 2025.
2. References to internal DeepSeek API endpoints.
3. Plaintext logs encompassing chat history, API keys, backend details, and operational metadata.
4. Identifiers indicating which DeepSeek service generated the logs.
5. Sources of log requests, exposing chat history, API keys, directory structures, and chatbot metadata logs.
This level of exposure posed critical risks, not only compromising user privacy but also potentially allowing attackers to escalate privileges within DeepSeek's environment.
Extended Timeline of Events
January 27, 2025: DeepSeek reported "large-scale malicious attacks" that disrupted the ability of new users to register on their platform. Existing users were able to continue using the service without interruptions.
January 29, 2025: An exposed ClickHouse database belonging to DeepSeek was discovered as publicly accessible without authentication, allowing unauthorized access to internal data. After being notified, DeepSeek restricted access to the database within approximately 30 minutes.
Preventive Measures and Recovery
This incident highlights the critical importance of securing the external perimeter and implementing robust authentication mechanisms. Leaving a database exposed without authentication creates significant security risks, including unauthorized access to sensitive information and potential privilege escalation.
To prevent similar incidents in the future, organizations should implement the following security measures:
1. Enforce Strong Authentication.
Ensure that all databases and internal systems are protected with strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and identity-based access controls.
2. Continuous Security Monitoring.
Deploy real-time monitoring tools to detect potential vulnerabilities and unauthorized access attempts.
3. Regular Security Audits.
Conduct periodic security audits to identify and mitigate potential weaknesses in the infrastructure.
4. Access Control Policies.
Restrict access to sensitive systems using the principle of least privilege (PoLP), ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to critical resources.
5. Data Encryption.
Encrypt data both at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access in case of a breach.
6. Automated Configuration Management.
Utilize Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) and automated security configuration tools to prevent misconfigurations that could expose sensitive assets.
7. Employee Security Awareness Training.
Educate employees on best cybersecurity practices to minimize the risk of human errors leading to security breaches.
Regarding the recovery phase, DeepSeek acted swiftly to secure the exposed database upon notification. However, the lack of detailed information about their follow-up remediation steps and long-term preventive measures makes it difficult to assess the completeness of their response.
Final Thoughts
The DeepSeek data breach highlights the dangers of an unsecured external perimeter and the absence of proper authentication controls. Leaving a database exposed without protection led to unauthorized access to sensitive data, increasing the risk of privilege escalation and potential system compromise.
This incident reflects a broader issue: AI companies are scaling into critical infrastructure providers at an unprecedented pace, often without the security frameworks necessary for such rapid expansion. As AI becomes deeply embedded in global business operations, the risks associated with handling sensitive data grow exponentially. Without stringent security measures comparable to those of public cloud and major infrastructure providers, AI-driven platforms remain vulnerable to misconfigurations, data breaches, and supply chain risks.
While DeepSeek swiftly restricted access to the exposed database, the lack of transparency regarding their remediation steps raises concerns about long-term security improvements. This case reinforces the urgent need for AI companies to adopt proactive security strategies—continuous monitoring, strict access controls, automated misconfiguration detection, and rigorous compliance standards must become industry norms. As AI adoption accelerates, so too must the commitment to securing the infrastructure that supports it.
Don’t just keep up with trends — be prepared for them!
Test our platform: https://a42.tech/